Better planning for sustainable urban growth and the use of natural solutions, careful management of protected areas near cities, and integration of nature into cities can help shift the recent trend of urbanization driven habitat loss. Without timely action to invest in sustainable cities, the potential result of business-as-usual could be significant biodiversity loss.
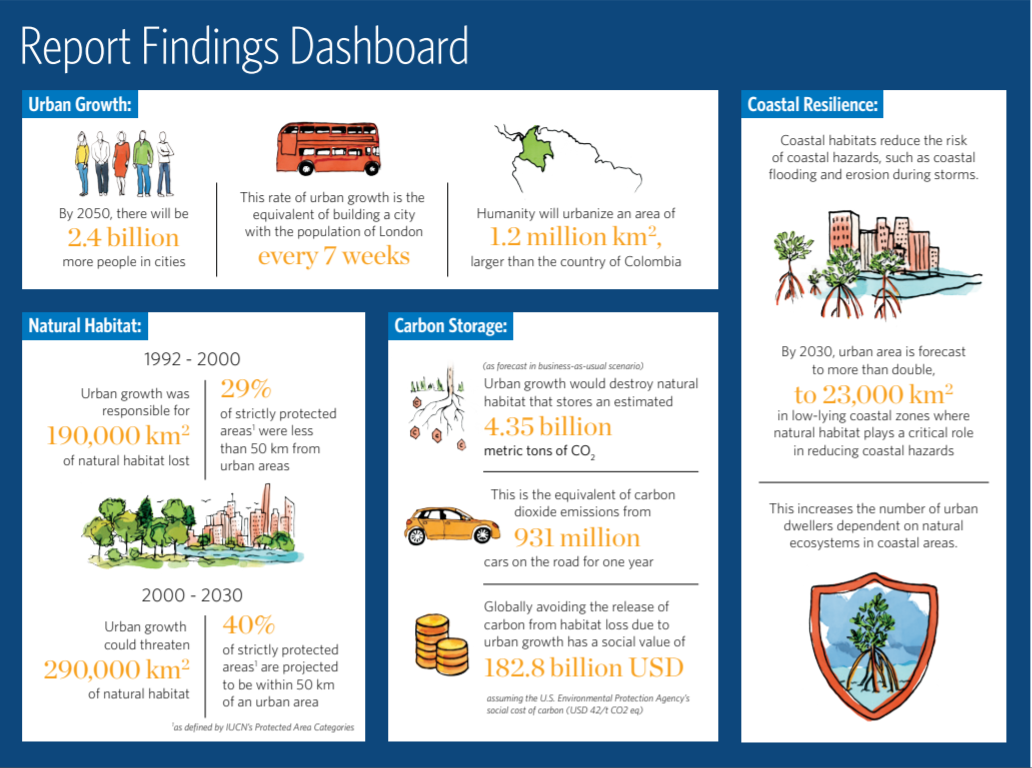
Urban growth could threaten 290,000 km2 of natural habitat between 2000 and 2030, according to a new report released in the lead up to the 2018 UN Convention on Biological Diversity Conference of the Parties meeting, Nature in the Urban Century. This is critical, as nature in and around cities is essential to maintain biodiversity and ensure human wellbeing, which depend on many benefits provided by nature.
Nature in the Urban Century looks into the challenge of managing urban growth, where and how much natural habitat could be lost, how protected areas will be affected, and implications for climate action. It finds that habitat loss will be extensive, especially in temperate and tropical forests, but that targeted action in these areas could prevent biodiversity loss. The biodiversity loss that does occur will be spatially concentrated, with global biodiversity levels heavily impacted by urban growth in a few specific places. In terms of protected areas, proximity with urban areas will likely increase negative impacts on nature and biodiversity as well as management costs. This is troublesome as 40% of strictly protected areas and 50% of loosely protected areas will be located within 50km of an urban area by 2030.
Solutions targeted at the city level should focus on the better planning and management of urban growth, with local governments integrated into national planning decisions so that planning at each level incorporates the benefits of nature and reinforces decisions at other levels. Other calls for action presented in the report are to empower cities to plan for a positive natural future, leverage international institutions, and create a Convention on Biological Diversity for the urban century.
Enlarge
Nature in the Urban Century report






