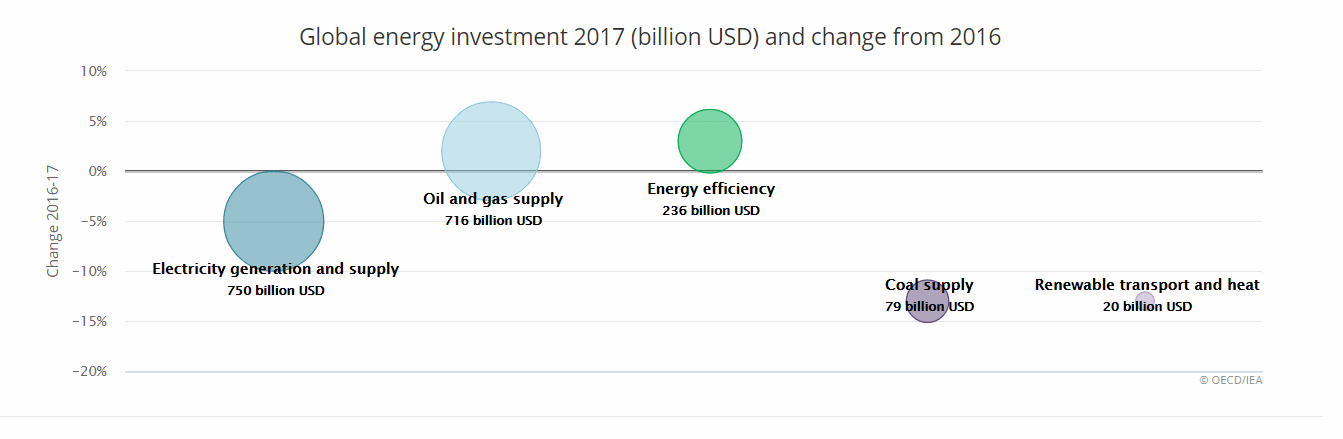According to the IEA’s World Energy Investment 2018 edition, in 2017 global energy investment declined for the third consecutive year, reaching USD 1.8 trillion (a fall of 2% in real terms compared with 2016).
Spending in coal, hydro and nuclear power have seen the stronger decline, while investments in energy efficiency improvements remained relatively immune from the overall downward trend. Here five points worth focusing on.
State actors’ lever on the rise
According to IEA analysis, almost 75% of global energy investments in 2017 was driven either by state-owned enterprises or private-led spending with public incentives. In some sectors such as renewables and energy efficiency, public policies are also increasingly influencing private decisions through policies, regulations and standards.
In global energy investment, China holds the (green) balance
For the third year in a row, China is the largest destination of energy investment, accounting for 20% of the global total. While the United States remained the second largest investing country thanks to an increase in shale oil and gas spending, China’s energy investment is increasingly focused on low-carbon electricity and energy efficiency. China halved its investments in new coal-fired plants, accounted for nearly 45% of global spending on solar PV and over half of all electric cars sold in 2017.
The future is electrifying
Electricity generation and supply got the lion’s share of energy investment in 2017 and exceeded the oil and gas supply for the second consecutive year. Among the few sectors that saw an increase in spending last year, electricity networks accounted for more than 40% of total investment in the electricity sector, up from one-third just five years ago.
Buying (less) renewables for less
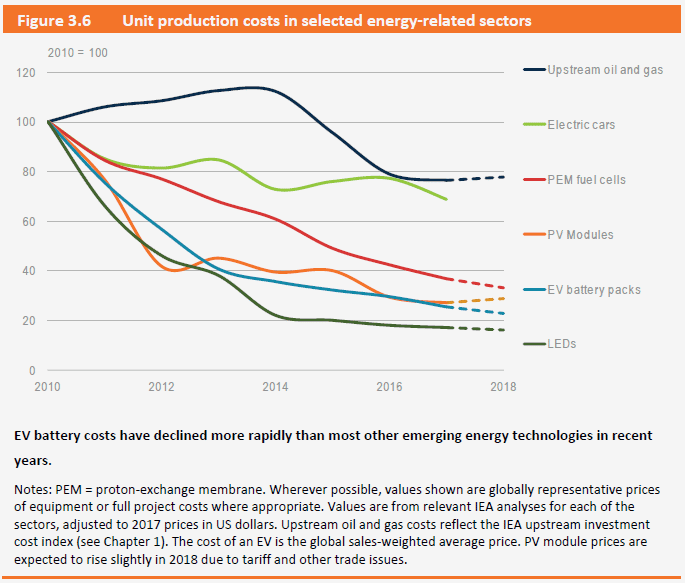
Digital innovations are reducing costs across the entire energy sector (see graph below). For clean energy products, such as batteries, solar PV panels and LED light bulbs, mass manufacturing and standardization have played a key role in driving costs down.
Together with technology improvements, these trends are making renewable energy expansion more and more affordable. Looking at power generation investment, the share of low-carbon energy sources (including nuclear) remained at a high level above 70%, with renewables making up over 65%. However, despite record levels of spending on solar PV, global investment in renewable energy declined by 7% in 2017 (in part exactly because of the lower prices). This is a “warning signal” for future capacity, generation and investment, IEA commentary stressed.
We are off track to meet climate goals
According to IEA analysis, there was a pause in the shift towards cleaner sources of energy supply and the current investment levels are not enough to meet global climate and sustainability goals. Even though the global economy is becoming less energy-intensive (with an estimated reduction of about 20% in final energy per unit of GDP compared to 90s’), the rebound of global growth has led CO2 emissions to rise for the first time in four years. Further progress in low-carbon energy sources is needed to drive energy transition towards what the IEA calls the “Sustainable Development Scenario”, in which the world meets climate objectives under the Paris Agreement, achieves universal energy access and substantially reduces the impacts of air pollution. Aviation, building envelopes, carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS), concentrating solar power, geothermal, heating and biofuels for transport are among those technologies that are off track.